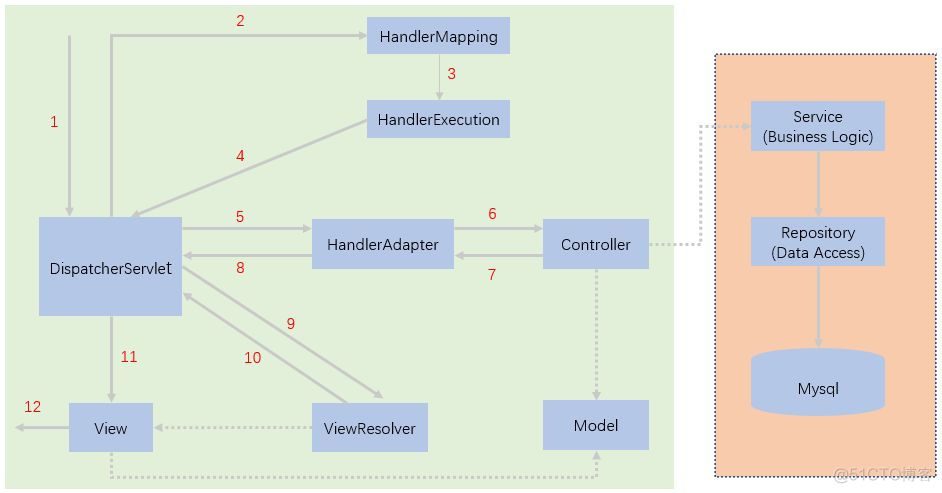
简要分析执行流程:
1.DispatcherServlet表示前置控制器,是整个SpringMVC的控制中心。用户发出请求,DispatcherServlet接收请求并拦截请求,
我们假设请求的url为:
http://localhost:9999/SpringMVC/input-product
如上url拆分成三部分:
http://localhost:9999 服务器域名
SpringMVC部署在服务器(http://localhost:9999)上的web站点
input-product表示控制器
通过分析,如上url表示为:请求位于服务器localhost:9999上的SpringMVC站点的input-product控制器
2.HandlerMapping为处理器映射。DispatcherServlet调用HandlerMapping,HandlerMapping根据请求url查找Handler
3.HandlerExecution表示具体的Handler,其主要作用是根据url查找控制器,如上url被查找控制器为:input-product
4.HandlerExecution将解析后的信息传递给DispatcherServlet,如解析控制器映射等
5.HandlerAdapter表示处理器适配器,其按照特定的规则去执行Handler
6.Handler让具体的Controller执行
7.Controller将具体的执行信息返回给HandlerAdapter,如ModelAndView
8.HandlerAdapter将视图逻辑名或模型传递给DispatcherServlet
9.DispatcherServlet调用视图解析器(ViewResolver)来解析HandlerAdapter传递的逻辑视图名
10.视图解析器将解析的逻辑视图名传给DispatcherServlet
11.DispatcherServlet根据视图解析器解析的视图结果,调用具体的视图
12.最终视图呈现给用户。
浅谈SpringMVC执行过程
https://blog.51cto.com/u_12302929/3325713
以上来自转载 看完觉得已经大致了解了 但是我还在得结合源码看一下
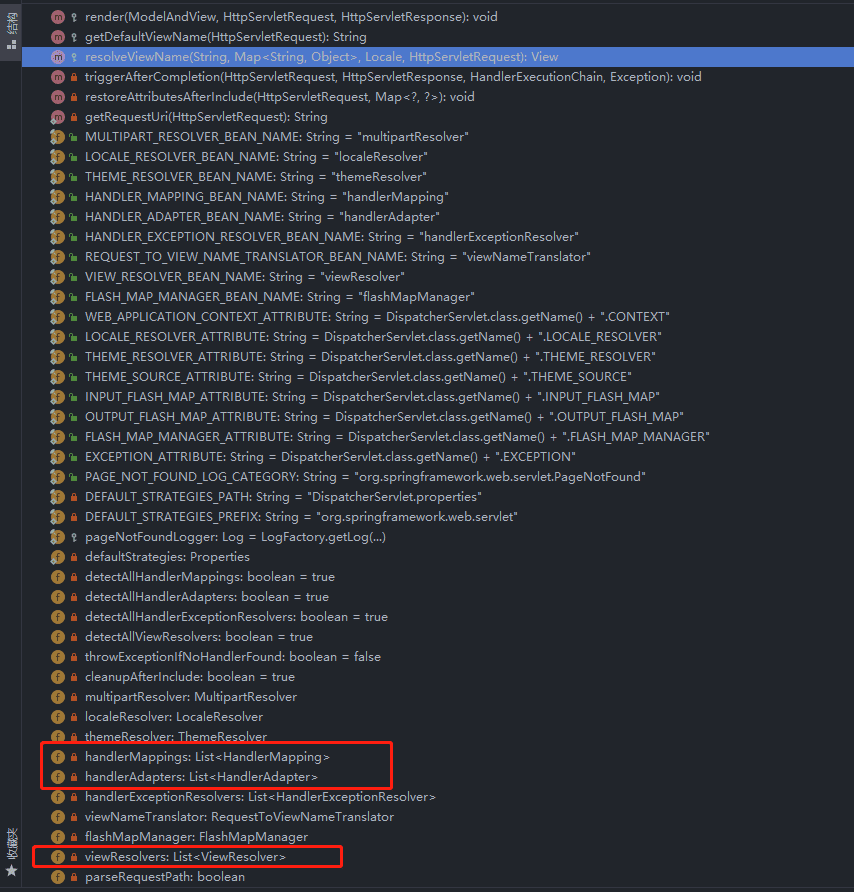
然后我就使用idea 查看了spring-webmvc-.3.10.jar下面的DispatcherServlet类
忽略方法 DispatcherServlet有一下这么多属性,大部分为static final 修饰的常量, 和上图相关的有
然后看一下最关键doDispatch方法
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* //所有HTTP方法都由该方法处理。由HandlerAdapters或处理程序本身来决定哪些方法是可接受的。
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//此处通过请求地址从handlerMappings中循环匹配 对应图中步骤2
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
//此处mappedHandler.getHandler()对应步骤3,
//getHandlerAdapter(**)方法从handlerAdapters中匹配HandlerAdapter 对应步骤5
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
//
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//拦截器处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//HandlerAdapter调用handle,由继承HandlerAdapter接口的controller处理,得到处理结果ModelAndView
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//设置viewName 如果
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//执行已注册拦截器的postHandle方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//处理调用结果 该结果要么是一个ModelAndView 要么是过程中的异常
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}processDispatchResult
还有很多地方没弄清楚 先记录在这 以后再丰富
